June 26, 2019 | Jola Glotzer
Screening for drugs against MERS
Twice CBC Awardees — Hyun Lee and Michael Johnson (UIC) — identify new compounds with a therapeutic potential against the coronavirus causing Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS)
Congratulations to the UIC team of Hyun Lee and Michael Johnson on a recent publication in Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, titled “Identification and design of novel small molecule inhibitors against MERS-CoV papain-like protease via high-throughput screening and molecular modeling.” The published work is partially attributed to a CBC HTS Award the team received in 2014 for a similarly titled project: “Identification and Development of Small Molecule Inhibitors Against Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV).”
Since its identification in 2012, MERS has taken more than 2200 lives; its overall fatality is about 35%. Additionally, following the initial cases restricted to the Middle East only, the virus continues to spread, mostly through travel-related pathways, causing sporadic outbreaks in other parts of the world. Hence, developing successful treatments and preventive measures is of global importance.
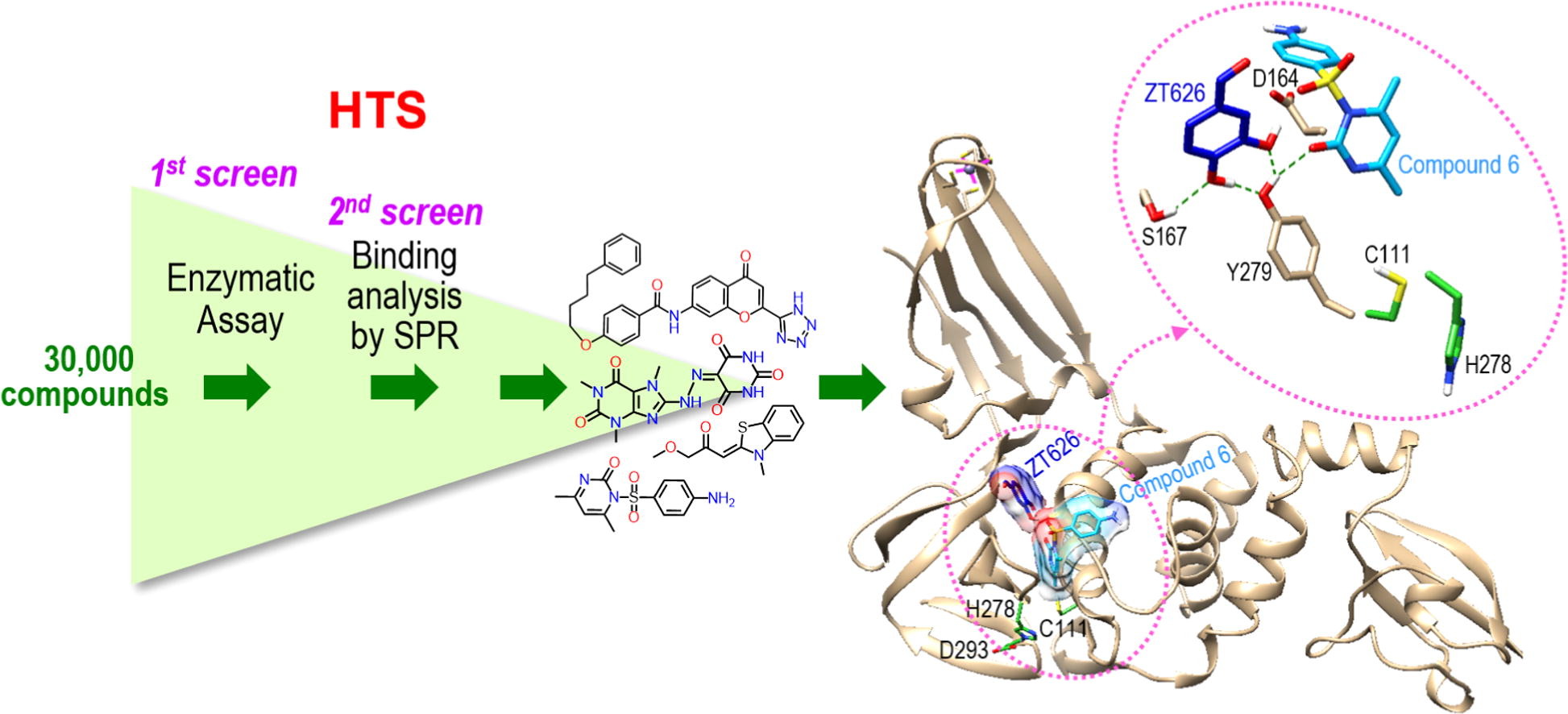
In the current study, using high-throughput screening (HTS) of several libraries, the authors identify two moderate inhibitors of the virus protease and one enhancer of the inhibitory action. The reported findings provide a good start-point towards designing and synthesizing more effective compounds and eventually therapeutics.
Lee, who is Director of Biophysics Core and Research Assistant Professor at the Department of Medicinal Chemistry and Pharmacognosy and Johnson, Professor Emeritus at the Center for Biomolecular Sciences, UIC, received another CBC HTS Award (2015) to conduct a screen for compounds against the methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA). Also listed below are Johnson’s CBC Awards and ties to the CBC, including serving on the CBC Catalyst Review Board (2006-2010). The CBC is grateful to Johnson for his time and commitment to the CBC programming and wishes him continuous successes in his scientific career.
Publication attributed to CBC funding*:
Lee H, Ren J, Pesavento RP, Ojeda I, Rice AJ, Lv H, Kwon Y, Johnson ME. Identification and design of novel small molecule inhibitors against MERS-CoV papain-like protease via high-throughput screening and molecular modeling. Bioorg Med Chem. 2019 May 15;27(10):1981-1989. (PubMed)
ABSTRACT
The development of new therapeutic agents against the coronavirus causing Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) is a continuing imperative. The initial MERS-CoV epidemic was contained entirely through public health measures, but episodic cases continue, as there are currently no therapeutic agents effective in the treatment of MERS-CoV, although multiple strategies have been proposed. In this study, we screened 30,000 compounds from three different compound libraries against one of the essential proteases, the papain-like protease (PLpro), using a fluorescence-based enzymatic assay followed by surface plasmon resonance (SPR) direct binding analysis for hit confirmation. Mode of inhibition assays and competition SPR studies revealed two compounds to be competitive inhibitors. To improve upon the inhibitory activity of the best hit compounds, a small fragment library consisting of 352 fragments was screened in the presence of each hit compound, resulting in one fragment that enhanced the IC50 value of the best hit compound by 3-fold. Molecular docking and MM/PBSA binding energy calculations were used to predict potential binding sites, providing insight for design and synthesis of next-generation compounds.
Graphical abstract. (Source: www.sciencedirect.com)
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Reported by Michael Johnson, during the CBC annual data collection (Dec. 2016) as partially funded by a CBC HTS Award (2014; see below).
Featured CBC Community member(s):
Hyun Lee and Michael Johnson, UIC
- CBC Accelerator Award (finalist, 2019):
▸ CBC Accelerator Network (CBCAN) meeting: Accelerator Award LOIs Round Three, Part Two
Michael Johnson (UIC) — Finalist and Presenter of his LOI at CBCAN - CBC Accelerator Award (finalist, 2018):
▸ CBC Accelerator Network (CBCAN) meeting: Accelerator Award proposals Round Two, Part Two
Michael Johnson (UIC) — Finalist and Presenter of his LOI at the CBCAN - CBC HTS Award (2015):
▸ Identification and Development of Small Molecules that Inhibit the VraSRT Operon, which Maintains Oxacillin Resistance in Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA)
PIs: Hyun Lee and Michael Johnson (UIC) - *CBC HTS Award (2014):
▸ Identification and Development of Small Molecule Inhibitors Against Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV)
PIs: Hyun Lee and Michael Johnson (UIC) - CBC Catalyst Award (2013):
▸ A novel antimicrobial strategy against methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA)
PIs: Robert Daum (UChicago) and Michael Johnson (UIC) - CBC HTS Award (2013):
▸ Virtual and High-throughput Screening for Anti-hemophilia Drugs that Target the Protein Z-dependent Protease Inhibitor-protein Z (ZPI-PZ) Interaction
PIs: Xin Huang, Steven Olsen and Michael Johnson (UIC) - CBC Tech Day (2012):
▸ Small Molecule Discovery in Academia
Michael Johnson (UIC) — Invited Speaker - CBC Scholar Award (2010):
▸ Meet the Scholar: Rima Chaudhuri
Michael Johnson (UIC) — Scholar’s Mentor - CBC Catalyst Review Board (2006-2010):
▸ Current membership
Michael Johnson (UIC) — Board Member

